In the modern healthcare landscape, data analysis is a powerful tool that drives better patient outcomes and more efficient care delivery. By harnessing the vast amounts of data generated in healthcare settings, professionals can uncover insights that lead to improved diagnoses, personalized treatments, and proactive care strategies. In this blog, we will explore how data analysis is transforming healthcare and enhancing patient outcomes.
The Role of Data in Healthcare
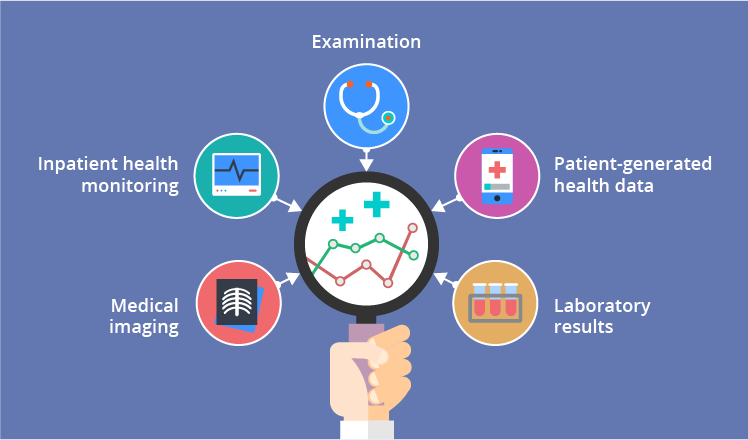
Healthcare data comes from a variety of sources, including electronic health records (EHRs), medical imaging, laboratory tests, wearable devices, and patient surveys. This data provides a comprehensive view of patient health, enabling healthcare providers to make more informed decisions.
Key Areas Where Data Analysis Improves Patient Outcomes
- Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses historical data and machine learning algorithms to forecast future health outcomes. By identifying patterns and trends, healthcare providers can predict the likelihood of diseases, hospital readmissions, and other critical events.
Applications:
- Disease Prevention: Identifying patients at high risk for chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease and implementing preventive measures.
- Early Intervention: Predicting potential complications in patients with existing conditions, allowing for early intervention and treatment adjustments.
- Resource Allocation: Forecasting patient admissions and optimizing staffing and resources to meet demand.
- Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine tailors treatments to individual patients based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle, and other factors. Data analysis helps identify the most effective treatments for specific patient profiles.
Applications:
- Pharmacogenomics: Analyzing genetic data to determine how patients will respond to certain medications, reducing adverse drug reactions.
- Targeted Therapies: Developing treatments that target specific genetic mutations or biomarkers, improving treatment efficacy.
- Custom Treatment Plans: Creating personalized care plans based on patient data, ensuring that treatments are tailored to individual needs.
- Clinical Decision Support
Clinical decision support systems (CDSS) provide healthcare professionals with data-driven insights and recommendations at the point of care. These systems use data analysis to enhance clinical decision-making.
Applications:
- Diagnostic Assistance: Analyzing patient data and medical literature to provide diagnostic suggestions and identify potential issues.
- Treatment Recommendations: Offering evidence-based treatment options and guidelines based on patient-specific data.
- Alert Systems: Generating alerts for potential drug interactions, allergies, and other critical information to prevent medical errors.
- Operational Efficiency
Data analysis improves operational efficiency in healthcare facilities, leading to better patient outcomes and reduced costs. By optimizing workflows and resource utilization, healthcare providers can deliver more effective care.
Applications:
- Appointment Scheduling: Analyzing patient appointment data to reduce wait times and improve scheduling efficiency.
- Supply Chain Management: Optimizing inventory levels and supply chain processes to ensure the availability of necessary medical supplies.
- Performance Monitoring: Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) to identify areas for improvement and implement quality control measures.
- Population Health Management
Population health management involves analyzing data from large groups of patients to identify health trends and improve community health outcomes. This approach focuses on preventive care and addressing social determinants of health.
Applications:
- Epidemiology: Monitoring and analyzing data on disease outbreaks and public health trends to inform policy and intervention strategies.
- Chronic Disease Management: Identifying at-risk populations and implementing community-based programs to manage chronic conditions.
- Health Disparities: Addressing social determinants of health by analyzing data on socioeconomic factors and health outcomes to create targeted interventions.
Challenges and Considerations
While data analysis offers significant benefits, there are challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring the confidentiality and security of patient data is paramount. Healthcare providers must comply with regulations such as HIPAA to protect patient information.
- Data Integration: Integrating data from multiple sources can be complex. Interoperability standards and technologies are needed to ensure seamless data sharing.
- Data Quality: High-quality data is essential for accurate analysis. Healthcare providers must implement robust data governance practices to maintain data accuracy and completeness.
- Ethical Considerations: Ethical considerations must be addressed when using data analysis in healthcare, particularly in areas like predictive analytics and personalized medicine.
Conclusion
Data analysis is revolutionizing healthcare by providing actionable insights that improve patient outcomes, enhance operational efficiency, and drive personalized care. By leveraging data, healthcare providers can make more informed decisions, predict and prevent health issues, and deliver tailored treatments that meet individual patient needs. Despite the challenges, the potential benefits of data analysis in healthcare are immense, promising a future where data-driven care leads to healthier populations and more efficient healthcare systems.
As technology continues to advance, the integration of data analysis into healthcare practices will only grow, offering new opportunities to enhance patient care and outcomes. Embracing data analysis in healthcare is not just a technological advancement; it is a critical step towards a more effective, efficient, and patient-centered healthcare system.