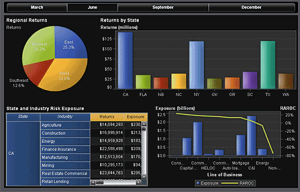
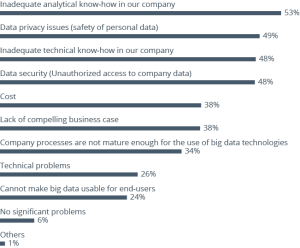
In today’s digital age, data is everywhere. From the websites we visit to the purchases we make, data is constantly being generated and collected. But what do we do with all this data? This is where data analysis comes in. By examining, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data, we can extract valuable insights that drive decision-making and innovation. Whether you’re a business owner, a student, or simply curious about how data shapes our world, understanding the basics of data analysis is essential.
What is Data Analysis?
Data analysis is the process of systematically applying statistical and logical techniques to describe, illustrate, condense, and evaluate data. It involves several steps, each crucial in ensuring that the final insights are accurate and meaningful.
Key Steps in the Data Analysis Process
- Data Collection
- The first step in data analysis is gathering data. This can be done through various methods such as surveys, experiments, observations, or extracting data from existing sources like databases and online repositories. The quality of your data collection process directly impacts the reliability of your analysis.
- Data Cleaning
- Once data is collected, it often needs to be cleaned. Data cleaning involves identifying and correcting errors, dealing with missing values, and ensuring that the data is consistent. This step is critical because inaccurate or inconsistent data can lead to incorrect conclusions.
- Data Exploration
- Data exploration, also known as exploratory data analysis (EDA), involves summarizing the main characteristics of the data. This can be done using statistical techniques and visualization tools like graphs and charts. EDA helps in understanding the data’s structure and identifying patterns, trends, and anomalies.
- Data Analysis
- The core of the data analysis process is the application of various techniques to extract insights. This can range from simple descriptive statistics to more complex inferential statistics and machine learning algorithms. The choice of techniques depends on the nature of the data and the questions you’re trying to answer.
- Data Interpretation
- Once the analysis is complete, the next step is to interpret the results. This involves drawing conclusions and making inferences based on the findings. It’s important to consider the context and ensure that the interpretations are logical and supported by the data.
- Data Presentation
- The final step is presenting the findings in a clear and understandable manner. This can be done through reports, dashboards, or presentations. Effective data visualization is key to making the insights accessible to a broader audience and facilitating informed decision-making.
Types of Data
Understanding the types of data is fundamental to data analysis. Data can be broadly categorized into two types: quantitative and qualitative.
- Quantitative Data: This type of data is numerical and can be measured and counted. Examples include height, weight, and sales figures. Quantitative data is often analyzed using statistical techniques.
- Qualitative Data: This type of data is descriptive and non-numerical. Examples include customer feedback, interview transcripts, and social media posts. Qualitative data is typically analyzed using thematic analysis or content analysis techniques.
Importance of Data Analysis
Data analysis is essential for several reasons:
- Informed Decision-Making: By analyzing data, organizations can make evidence-based decisions that are more likely to lead to successful outcomes.
- Identifying Opportunities and Risks: Data analysis helps in identifying trends and patterns that can reveal new opportunities or potential risks.
- Improving Efficiency: Through data analysis, businesses can optimize processes, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
- Enhancing Customer Experience: Analyzing customer data can provide insights into preferences and behaviors, enabling personalized experiences and improved customer satisfaction.
Common Tools for Data Analysis
There are various tools available for data analysis, each with its strengths and use cases:
- Excel: A versatile tool for basic data analysis and visualization.
- Python: A powerful programming language with libraries like pandas, NumPy, and matplotlib for data manipulation and visualization.
- R: A statistical programming language used for advanced data analysis and visualization.
- SQL: A language used for managing and querying relational databases.
- Tableau: A data visualization tool that helps create interactive and shareable dashboards.
- Power BI: Microsoft’s business analytics tool for visualizing and sharing insights across an organization.
Conclusion
Data analysis is a powerful tool that can transform raw data into actionable insights. By understanding the basics of data analysis, you can unlock the potential of data to drive informed decisions, identify opportunities, and solve complex problems. Whether you’re analyzing data for business, research, or personal interest, mastering the fundamentals of data analysis is a valuable skill in today’s data-driven world.
Embrace the power of data and start your journey into the fascinating world of data analysis. With the right techniques and tools, you can turn data into a powerful asset that fuels innovation and success.